Wouldn’t it be great if your words could automatically be translated into another language? Well, that dream is here! Today’s modern translation agencies work with a system called neural machine translation (NMT).
NMT is cutting-edge machine learning translation technology based on neural network techniques. The technology relies on deep neural networks and AI to train neural models, resulting in highly accurate translations. But this is only one type of machine translation.
Other types of machine translation include the following:
- Rule-based machine translation (RBMT): is based on language and grammar rules lined with dictionaries to generate translations.
- Statistical machine translation: this technology relies on statistical models created from the analysis of extensive databases of multilingual content.
Table of Contents
How Neural Machine Translation Works

Neural machine translation uses neural networks to predict patterns for generating the correct translation into the target language. A neural network is a series of interconnected nodes (neurons) that are patterned after the human brain.
Neutral machine translations rely on deep neural networks that use an encoder-decoder architecture (network). The network helps cluster and classify information, grouping data according to similarities in the input data. This process is similar to the work done by neural networks in the human brain.
Before the translation is done, the NMT software is given training data, which includes examples of translations for a certain text. Using this data, the software is trained to produce the most accurate translation possible.
Benefits of Neural Machine Translation
There are many advantages to using NMT over traditional machine translation methods. NMT is quite different. The main difference is that NMT can study large amounts of data, such as large amounts of text, during the translation process. Traditional translation methods don’t have this capability. Instead, these methods use a literal translation method, which does not follow the subtleties of how humans use language.
NMT offers a more contextualized translation form than traditional machine learning methods. This is one of the reasons that neural machine translation is faster than other translation methods.
In addition, NMT requires less memory for translation work and doesn’t require as many engineering and design choices. The result is a more accurate, faster translation that offers a cost-effective solution over traditional translation methods.
The overall effect that NMT has had on translation is stunning. This technology is quickly changing the world economy and casting down language barriers around the world.
Through the advances of NMT, small businesses can further their reach like never before. They now can reach a global market, even with smaller operational budgets.
In addition, it’s now possible to translate thousands of documents into several languages. In the past, this amount of work would have taken weeks for a team of translators and linguists. Today, however, almost instant translations are possible on a large scale.
What’s more, businesses in the farthest reaches of the world now have the ability to reach new markets. With accurate, reliable translations, they can reach customers on the other side of the globe in their own language(s). The result is lower friction for global commerce and increased opportunities for remote customers and businesses.
Use Cases and Applications of Neural Machine Translation
Neural machine translation is currently being used in a broad number of translation applications. In this section, we’ll take a look at some different use cases and applications of NMT in real-life situations.
Google Translate

We’ll start off with a quick overview of Google Translate, which is a multilingual NMT service created by Google. The tool is used to translate all kinds of documents, text, and more.
Google Translate offers different interfaces, including web and mobile apps for Android and iOS. The company also allows developers to build browser extensions and other software apps with its API. The NMT currently supports over 133 languages.
Microsoft Translator

Microsoft Translator is another multilingual machine translation service that’s cloud-based. The service was developed by Microsoft and is part of their Microsoft Cognitive Services. The NMT has been integrated across consumer, developer, and enterprise products. It now works with over 100 languages and can translate between many languages and language varieties.
This service also supports a variety of speech translation systems, including Skype Translator, Skype for Windows Desktop, and the Microsoft Translator apps for Android & iOS.
DeepL

Deepl is another popular NMT translation service that’s used by both businesses and individuals. The app has earned a good reputation for its accurate, nuanced translations. The service features an intuitive interface.
This NMT service works with about 26 languages and has the following features:
- Document translation
- App integration
- Website translation widget
- Encrypted cloud storage
Related Post: Discover The Top Translator Tools to Boost Your Productivity
Challenges and Limitations of Neural Machine Translation
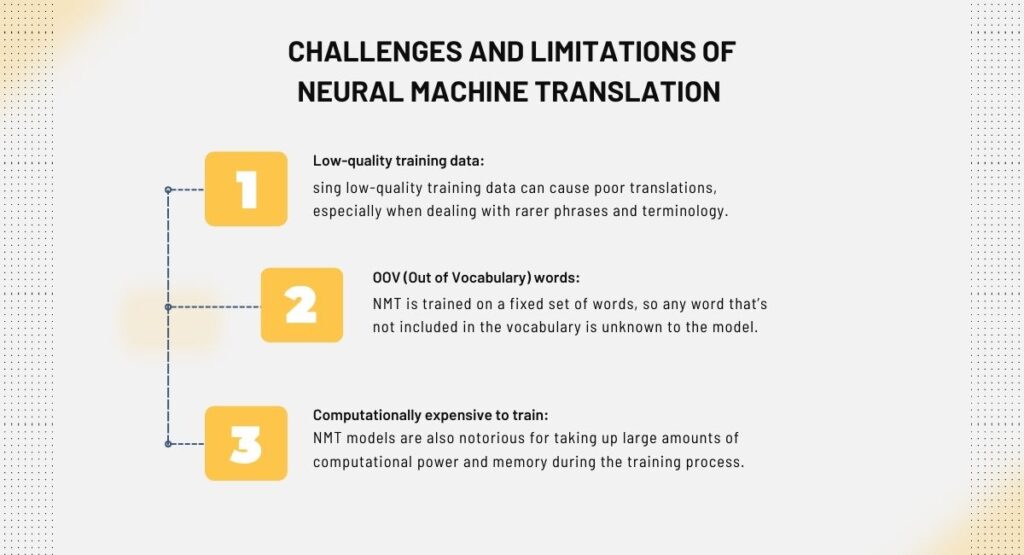
While NMT offers many benefits, it also comes with certain challenges and limitations.
Low-quality training data: using low-quality training data can cause poor translations, especially when dealing with rarer phrases and terminology.
OOV (Out of Vocabulary) words: NMT is trained on a fixed set of words, so any word that’s not included in the vocabulary is unknown to the model. This can result in low translation quality, where the NMT may even generate non-sense translations.
Computationally expensive to train: NMT models are also notorious for taking up large amounts of computational power and memory during the training process. The issue is that scaling the technology is more challenging regarding large-scale and real-time applications.
When it comes to NMT’s limitations, the most serious issue is the model generating translations that are fluent but not accurate. This is especially a problem when dealing with idioms and other specialized language. The NMT may produce a literal translation that sounds natural; however, the meaning is not correct.
Another area for improvement is that deep neural networks can be complicated for scientists to understand. The intricacy of the neural network can be challenging to discern, and difficult to understand why a specific translation was generated.
The last major limitation of neural machine translation is that the language models require high-quality and large amounts of training data. Maintaining and collecting the data can take time, resulting in additional costs.
The Future of Neural Machine Translation
The future looks bright for neural machine translation. What does the future bring?
Improved accuracy and quality: over time, it’s expected that NMT will continue to improve and become more accurate, generating higher-quality translations.
Multilingualism: as the need for multilingual tools increases, NMT offers more businesses and individuals access to these cost-effective, accurate translation tools. NMT systems are expected to become more advanced and offer support for more languages and language pairs.
Integration with other technologies: the future also sees more integration of NMT with other technologies, such as natural language processing, sentiment analysis, and speech recognition.
The potential impact of NMT will continue to grow, especially in businesses wanting to reach new, global markets. The travel industry, too, will have access to cost-effective translation tools for improved communication with customers.
Moreover, neural machine translation will also have a significant impact on education, which will have the ability to source texts from other languages and cultures. The technology will also make it easier than ever for students to learn new languages.
Such broad applications paint a bright future for neural machine translation technology.
Conclusion
Neural machine translation technology has significantly changed how translations are generated. The technology offers high-quality, accurate translations in many cases. However, the accuracy of the generated translation is based on the quality and quantity of the input database.
While specific challenges must be overcome, NMT is becoming a popular translation technology around the globe and will continue to do so for the foreseeable future.
